For those with diabetes, the feet can become silent battlegrounds where high blood sugar can quietly lead to nerve damage, poor circulation, and serious risks if left unchecked. This article will cover the essentials of diabetic foot syndrome, including strategies for managing symptoms, reducing risks, and protecting foot health.
If you or a loved one has diabetes, schedule a visit with our doctors at Bluebonnet Foot and Ankle Institute in Austin, Texas, to learn more about the importance of foot care.
Diabetic Foot Syndrome (DFS) occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels lead to nerve damage, poor blood flow, and an increased risk of infections in the feet. Patients with diabetes mellitus often experience peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) that reduces their ability to feel sensations in their feet, along with diminished blood circulation, which impairs the body’s ability to heal.
DFS can manifest in various ways, from numbness and pain to visible changes like foot ulcers and discoloration in the affected foot. Without timely intervention, DFS can result in severe complications, including infections, tissue death, and even amputation.
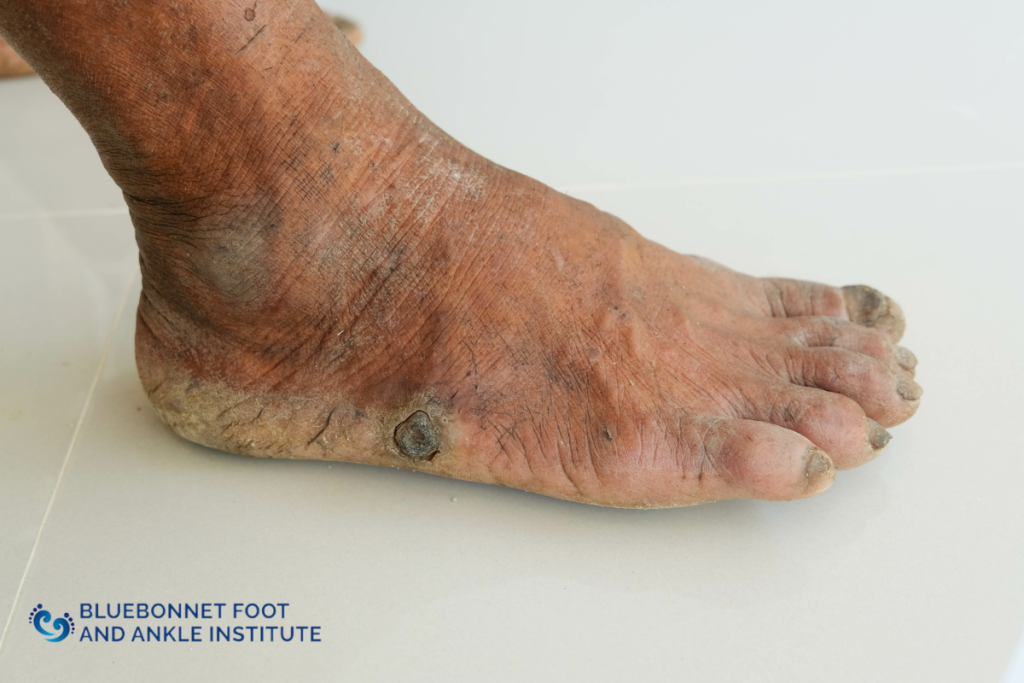
Several factors associated with diabetes can lead to DFS. The primary cause is high blood sugar, which can damage blood vessels and nerves over time. In diabetic neuropathy, for instance, nerves become impaired, making it difficult for individuals to feel sensations such as pain or temperature changes in their feet. This lack of sensation can make small injuries go unnoticed, leading to more severe issues like foot ulcers.
Poor circulation, another significant factor, restricts blood flow to the feet, slowing down the healing process and increasing the risk of infection. Blood vessels in patients with diabetes often become narrowed or blocked by blood clots, which can also contribute to swelling and an increased risk of foot infection. These combined factors make it essential for patients with diabetes to monitor their foot health closely.
DFS symptoms can vary widely but often start subtly. It is crucial for patients with diabetes to watch for any of the following signs:
These symptoms may worsen without intervention. Peripheral neuropathy often masks early signs, allowing minor injuries or infections to go unnoticed and untreated.
For those with diabetes, even small foot issues should not be ignored. Schedule an appointment with a podiatrist if you experience any of the following:
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent minor issues from progressing into serious complications, protecting foot health and overall well-being.
If left untreated, DFS can lead to significant complications that impact the entire foot and even overall health. Some of the potential complications include:
Proactive treatment and preventive care are essential to avoid these severe outcomes.
Swelling in the feet and ankles is common in patients with diabetes due to poor blood circulation. As blood vessels narrow, the affected foot can become swollen and painful. High blood sugar contributes to this by damaging blood vessels, causing fluids to accumulate in the lower extremities.
Swelling may worsen when patients remain inactive for prolonged periods or spend long hours standing. Patients should monitor swelling closely, as it can signal circulation issues or the development of more severe conditions, including blood clots and infections.
Managing DFS focuses on preventing further complications and maintaining healthy blood flow. Here are several ways to manage symptoms effectively:
If you’re experiencing symptoms of diabetic foot syndrome or have concerns about your foot health, schedule an appointment with Bluebonnet Foot and Ankle Institute in Austin, Texas. Our team is here to help you achieve healthier feet and a better quality of life with expert care and personalized support. Contact us today!
Medically reviewed by Liza Chabokrow, DPM